What is Blockchain Technology: Types, Key Components & Features!

Have you ever stopped to think about how data or payments can flow securely and transparently across the globe without delays or intermediaries?
In today’s blog, we’ll explore how blockchain is reshaping industries, simplifying payments, and unlocking potential like never before. Stay with us to dive into the details that matter most to you!
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that records transactions between computers. Unlike traditional systems controlled by banks or central authorities, blockchain relies on peer-to-peer networks to validate and store data securely.
Each “block” contains transaction details and is linked to the previous one, forming a “chain.” Once recorded, this data becomes immutable, ensuring tamper-proof records and unparalleled transparency.
Blockchain has made waves in crypto transactions, smart contracts, supply chain management, and even healthcare.
What is the Importance of Blockchain Technology?
The significance of blockchain lies in its ability to address the inefficiencies of traditional systems.
- Global Usage: Over 420 million people worldwide are using blockchain-powered cryptocurrencies as of 2023.
- Faster Transactions: Traditional bank transfers take 3–5 days, while blockchain payments are completed within minutes.
- Cost Savings: Businesses save up to 70% on transaction fees by using blockchain for payments.
Imagine this: A business in Kenya receives payment from a client in Canada instantly and securely without paying exorbitant intermediary fees. Blockchain eliminates barriers, making transactions seamless and accessible.
 Source: Zippia
Source: Zippia
What are the Features of Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is built on fundamental principles that make it secure, transparent, and revolutionary. A closer look at its distinguishing traits:
1. Decentralization
Blockchain’s decentralized nature ensures no single entity has control over the system. Instead, power is distributed across a network of participants (nodes). This eliminates intermediaries like banks or centralized organizations, reducing costs and risks.
Decentralization makes transactions faster, more secure, and free from bottlenecks, enabling seamless global payments and empowering users with autonomy.
Read More: Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
2. Immutability
Immutability means that once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature creates a permanent and reliable record of transactions, ensuring trust and authenticity.
It’s particularly valuable in industries like supply chain, where every step in the process is logged transparently, and in finance, where tamper-proof records eliminate fraud and discrepancies.
3. Transparency
Blockchain’s transparency ensures that all transactions are recorded on a public ledger, visible to all participants in the network. This openness fosters trust and accountability by enabling real-time verification of transactions.
For example, companies can use blockchain to track goods throughout the supply chain, allowing consumers to trace the origins of their purchases, ensuring ethical sourcing, and reducing fraud.
4. Security
Security is a cornerstone of blockchain, with advanced cryptographic algorithms protecting every transaction. Each block is encrypted and linked to the one before it, making tampering nearly impossible.
This level of security is why blockchain is widely trusted for managing crypto payments, safeguarding digital wallets, and protecting sensitive data in industries like healthcare and finance.
The Key Components of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is a sophisticated system composed of several integral components that work together to ensure its functionality, security, and efficiency. Let's delve into these key components:

1. Distributed Ledger
At the heart of blockchain lies the distributed ledger—a decentralized database that records all transactions across a network. Each participant maintains a copy of this ledger, ensuring transparency and reducing the need for a central authority. This structure allows for real-time updates and verifiable histories of all transactions, fostering trust among participants.
2. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Network
The Peer-to-Peer network facilitates direct interaction between nodes (participants) without intermediaries. In this decentralized model, each node can function as both a client and a server, sharing and storing data collectively. This setup enhances the system's resilience, as there is no single point of failure, and ensures continuous operation even if some nodes go offline.
3. Consensus Mechanism
To maintain consistency across the distributed ledger, blockchain employs consensus mechanisms—protocols that help nodes agree on the validity of transactions. Common methods include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Nodes (miners) solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions, ensuring security but requiring significant computational power.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on the number of tokens they hold and are willing to "stake," promoting energy efficiency and scalability. These mechanisms prevent double-spending and ensure that the network operates smoothly without a central authority.
4. Nodes
Nodes are the individual devices—computers, servers, or other digital equipment—that participate in the blockchain network. Each node maintains a copy of the distributed ledger and contributes to the network's security and integrity by validating and relaying transactions. The decentralized nature of nodes ensures that the system is robust against attacks and failures.
5. Cryptography
Cryptography underpins the security of blockchain, employing mathematical techniques to protect data and communications. Key cryptographic elements include:
- Public and Private Keys: These keys enable secure transactions, with the public key serving as an address and the private key authorizing transactions.
- Digital Signatures: They verify the authenticity and integrity of a message, ensuring that the sender is genuine and the message hasn't been altered.
- Hash Functions: These functions convert input data into a fixed-size string of characters, which acts as a unique identifier for the data, ensuring its integrity.
By integrating these components, blockchain technology provides a secure, transparent, and decentralized platform for various applications, revolutionizing how data and transactions are managed across multiple industries.
Types of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology isn’t one-size-fits-all—it’s as versatile as the industries it serves. Depending on the level of access, control, and transparency required, blockchain is categorized into different types. Let’s break down the key types of blockchain systems:
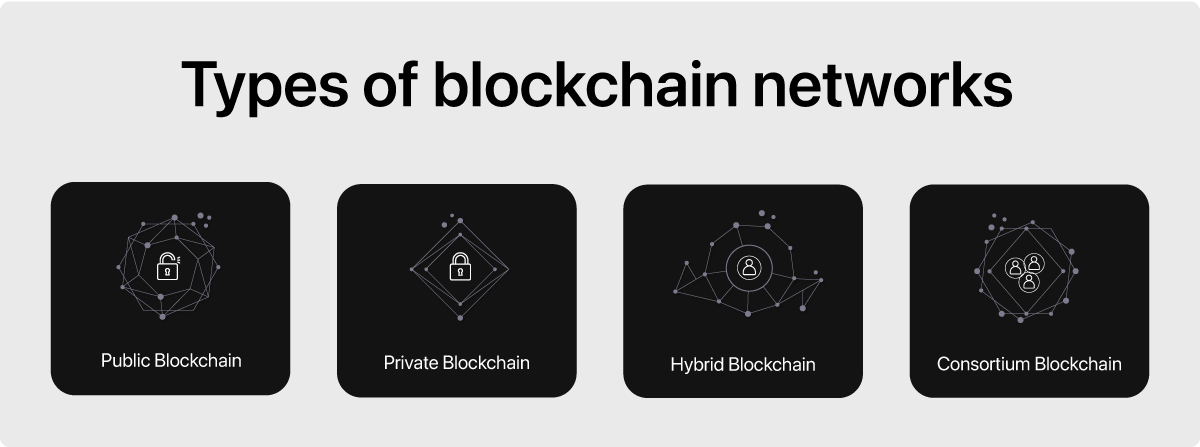
1. Public Blockchain
Public blockchains are open networks where anyone can join, view, and participate. These systems, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, operate on transparency and decentralization, making them ideal for cryptocurrency transactions and other applications requiring trustless operations.
2. Private Blockchain
Private blockchains are restricted networks accessible only to specific users or organizations. These systems are commonly used for internal business processes, providing enhanced privacy and control while maintaining the efficiency of blockchain technology.
3. Consortium Blockchain
Consortium blockchains are managed collaboratively by a group of organizations. This type of blockchain balances transparency and control, making it suitable for industries like finance and healthcare, where multiple stakeholders need shared access to secure data.
4. Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchains combine the best of public and private systems. They allow certain data to remain private while enabling public verification where needed. This flexibility makes hybrid blockchains perfect for scenarios where businesses need both transparency and confidentiality, such as in supply chain management
How Blockchain Impacts Payments
Blockchain’s greatest impact lies in its ability to revolutionize payments:
- Cross-Border Transactions: Over $1 trillion in cross-border crypto payments were made in 2023 alone. Blockchain eliminates delays and reduces fees, making it a top choice for businesses with global operations.
- E-commerce Integration: By 2025, over 60% of global merchants are expected to accept crypto payments, driven by blockchain’s ability to process payments efficiently and securely.
- Coins in Payments: Cryptocurrencies like USDT and USDC provide stability, making them ideal for everyday payments. For example, in countries like El Salvador and Switzerland, businesses already accept crypto for groceries, coffee, and even utility bills.
How Paycio is Simplifying Financial Transactions Using Blockchain
Paycio exemplifies how blockchain simplifies financial transactions for both individuals and businesses. Here's how:
- Versatile Transactions: Paycio supports crypto payments using Bitcoin, Ethereum, USDT, and USDC, ensuring compatibility with diverse user needs.
- Business Payment Optimization: Merchants can seamlessly convert crypto payments into fiat currency and receive direct bank settlements without third-party delays.
- Offline Accessibility: With Paycio, offline payments can be processed even without internet connectivity, ensuring reliability in any situation.
- Global Reach: Users can send and receive payments globally, connecting businesses and consumers across borders with ease. Paycio bridges the gap between blockchain technology and everyday needs, making it accessible and practical for everyone.
Whether you’re simplifying crypto operations or exploring new business possibilities, now is the time to sign up with paycio and experience the future of smart payments.
Related blogs

What is Blockchain Technology: Types, Key Components & Features!
Explore how blockchain technology is transforming traditional payments and its fundamental elements of decentralization, immutability, and security
Recent Blogs


















